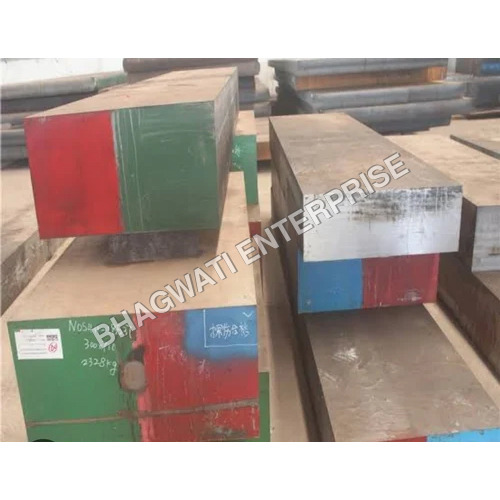
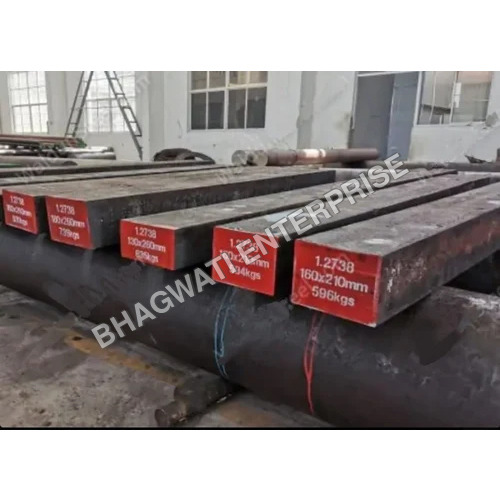
Cold Work Tool Steel D2 Block For Plastic Mould Industry
Cold Work Tool Steel D2 Block For Plastic Mould Industry Specification
- Product Name
- Other
- Steel Type
- Tool Steel
- Grade
- D2/D3
- Shape
- Plate
- Surface
- Coated
- Application
- Other
Cold Work Tool Steel D2 Block For Plastic Mould Industry Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 100 Kilograms
- Payment Terms
- Cheque, Cash Against Delivery (CAD), Cash on Delivery (COD), Cash Advance (CA), Cash in Advance (CID)
- Supply Ability
- 5000 Kilograms Per Month
- Delivery Time
- 2 Days
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- Packaging Details
- Loose
- Main Export Market(s)
- Asia
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
- Certifications
- Mill T.C. / Lab T.C.
About Cold Work Tool Steel D2 Block For Plastic Mould Industry
About Our Company Leveraging on our vast Industrial Experience We Bhagwati Enterprise, are acknowledged as one of the leading Supplier, Exporter, Trader, Importer & Wholesaler/Distributor of the Industry. Since 1992 we are dealing in a broad assortment of Alloy Steel, Tool Steel, Die Steel, Steel Bars, Carbon Steel Round Bars, SAE 8620 Steel Round Bars, EN Series Steel Round Bars, , AISI Series Steel Round Bars, Flat Bars, Free Cutting Steel, Steel Plates & Nitriding Steel. House Of MS Seamless Pipe To maintain the flawless of the products our Vendors Employ Cutting edge technology and tools in the manufacturing process. After this, all these products
D2 tool steel is a high-carbon, high-chromium cold work tool steel known for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and toughness. Heres a comprehensive description:
Chemical Composition
- Carbon (C) 1.40-1.60%
- Chromium (Cr) 11.00-13.00%
- Molybdenum (Mo) 0.70-1.20%
- Vanadium (V) 0.10-0.30%
- Manganese (Mn) 0.60-0.90%
- Silicon (Si) 0.60-0.90%
- Phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S) Max 0.03% each
Properties
- Hardness D2 tool steel is known for its high hardness, typically reaching 60-62 HRC (Rockwell Hardness C) after heat treatment.
Applications
- Cutting Tools Widely used in manufacturing cutting tools such as knives, shear blades, and dies for cold working.
- Dies and Molds Suitable for making dies and molds that require high wear resistance and dimensional accuracy.
- Punches and Dies Employed in various stamping and punching applications.
- Forming Tools Used for tools involved in cold forming processes due to its durability and wear resistance.
Heat Treatment
- Annealing Typically done at around 850-900C (1562-1652F), followed by slow cooling to relieve stresses and improve machinability.
- Hardening Heat to 1020-1040C (1868-1904F), followed by quenching in oil or air.
- Tempering Usually performed at temperatures between 150-200C (302-392F) to achieve the desired hardness and toughness while reducing brittleness.
Standards and Grades
- Standards D2 is commonly referenced in standards such as ASTM A681 and DIN 1.2379.
- Grades It is often available in various forms, including bars, plates, and sheets.
-
Grade D2 Cold Work Steel
-
Oil Hardened Tool Steel (O1)
-
Tool Steel Flats and Round Bars
-
Machinable Cold Work Steel
-
ISO Standard Tool Steels
-
Tool Steel Blocks for Die Manufacturing
-
Cold Work Tool Steel
-
High-performance Tool Steel
-
High Hardness Tool Steel
-
Cold Work Die Steel
-
Tool Steel Grade [e.g., D2, O1, A2, SKD11]
-
Hardened Cold Work Steel
- Die Steel Manufacturer in Vadodara Gujrat
- Tool Steel Supplier India
- Exporter of Die Steel from India
- Leading Cold Work Tool Steel Supplier
- Industrial Tool Steel Supplier
- Exporter of Cold Work Tool Steels
- OEM Tool Steel Manufacturer
- Buy Cold Work Tool Steel Online
- Cold Work Tool Steel Supplier
- Wholesale Tool Steel Distributor in Gujrat
- Industrial Steel for Die Making
- Tool Steel Exporter
- Cold Work Tool Steel Manufacturer
- Custom Cut Tool Steel
- Ready Stock Tool Steel in Vadodara
- Bulk Tool Steel Supply in Gujrat
-
The top Tool Steel manufacturers are
-
The top Cold Work Tool Steel Suppliers in India.


Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Industrial Steel Block Category
Stainless Steel Forging Block
Minimum Order Quantity : 100 Kilograms
Steel Type : Stainless Steel
Surface : Coated
Grade : 304
Application : Cosmetic Products
Plastic Mould Steel Block
Price 280.00 INR / Kilograms
Minimum Order Quantity : 100 Kilograms
Steel Type : Stainless Steel
Surface : Polished
Grade : P20
Application : Other






 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS